React Live
A flexible playground for live editing React components
README

React Live
A flexible playground for live editing React code
React Live brings you the ability to render React components with editable source code and live preview.
The library is structured modularly and lets you style and compose its components freely.
Usage
Install it with npm install react-live or yarn add react-live and try out this piece of JSX:
- ``` js
- import {
- LiveProvider,
- LiveEditor,
- LiveError,
- LivePreview
- } from 'react-live'
- <LiveProvider code="<strong>Hello World!</strong>">
- <LiveEditor />
- <LiveError />
- <LivePreview />
- </LiveProvider>
- ```
Demo
FAQ
How does it work?
It takes your code and transpiles it with Sucrase, while the code is displayed using [use-editable](https://github.com/FormidableLabs/use-editable) and the code is highlighted using [prism-react-renderer](https://github.com/FormidableLabs/prism-react-renderer).
The transpiled code is then rendered in the preview component (LivePreview), which does a fake mount if the code
is a React component.
Prior to v3.0.0, earlier versions of the library used different internals. We recommend using the latest version you can.
| |Version|Supported | |Editor | |Transpiler |
|---|---|---|
| |-------|-----------------------|--------------------------|---------- | ||
| |v3.x.x | |v17.x.x | |`use-editable` |
| |v2.x.x | |v16.x.x | |`react-simple-code-editor`|`Bublé` |
Please see also the related Formidable libraries:-
What code can I use?
The code can be one of the following things:
- React functional components with Hooks
- React component classes
If you enable the noInline prop on your LiveProvider, you’ll be able to write imperative code,
and render one of the above things by calling render.
How does the scope work?
The scope prop on the LiveProvider accepts additional globals. By default it injects React only, which
means that the user can use it in their code like this:
- ``` js
- // ↓↓↓↓↓
- class Example extends React.Component {
- render() {
- return <strong>Hello World!</strong>
- }
- }
- ```
But you can of course pass more things to the scope. They will be available as variables in the code. Here's an example using styled components:
- ``` js
- import styled from 'styled-components';
- const headerProps = { text: 'I\'m styled!' };
- const scope = {styled, headerProps};
- const code = `
- const Header = styled.div\`
- color: palevioletred;
- font-size: 18px;
- \`
- render(<Header>{headerProps.text}</Header>)
- `
- <LiveProvider code={code} scope={scope} noInline={true}>
- <LiveEditor />
- <LiveError />
- <LivePreview />
- </LiveProvider>
- ```
- ``` js
- import { MyButton } from './components/MyButton';
- const scope = { MyButton };
- const code = `
- <MyButton />
- `
- <LiveProvider code={code} scope={scope}>
- <LiveEditor />
- <LiveError />
- <LivePreview />
- </LiveProvider>
- ```
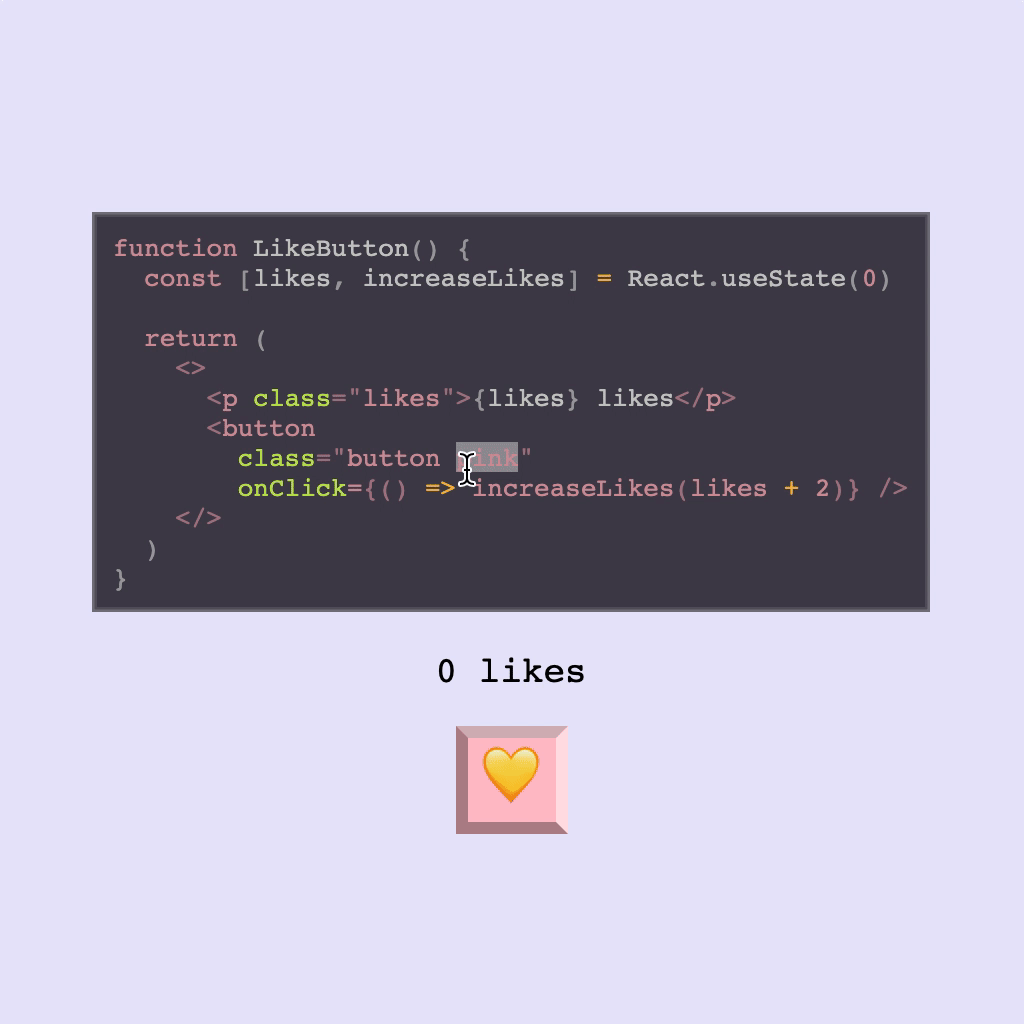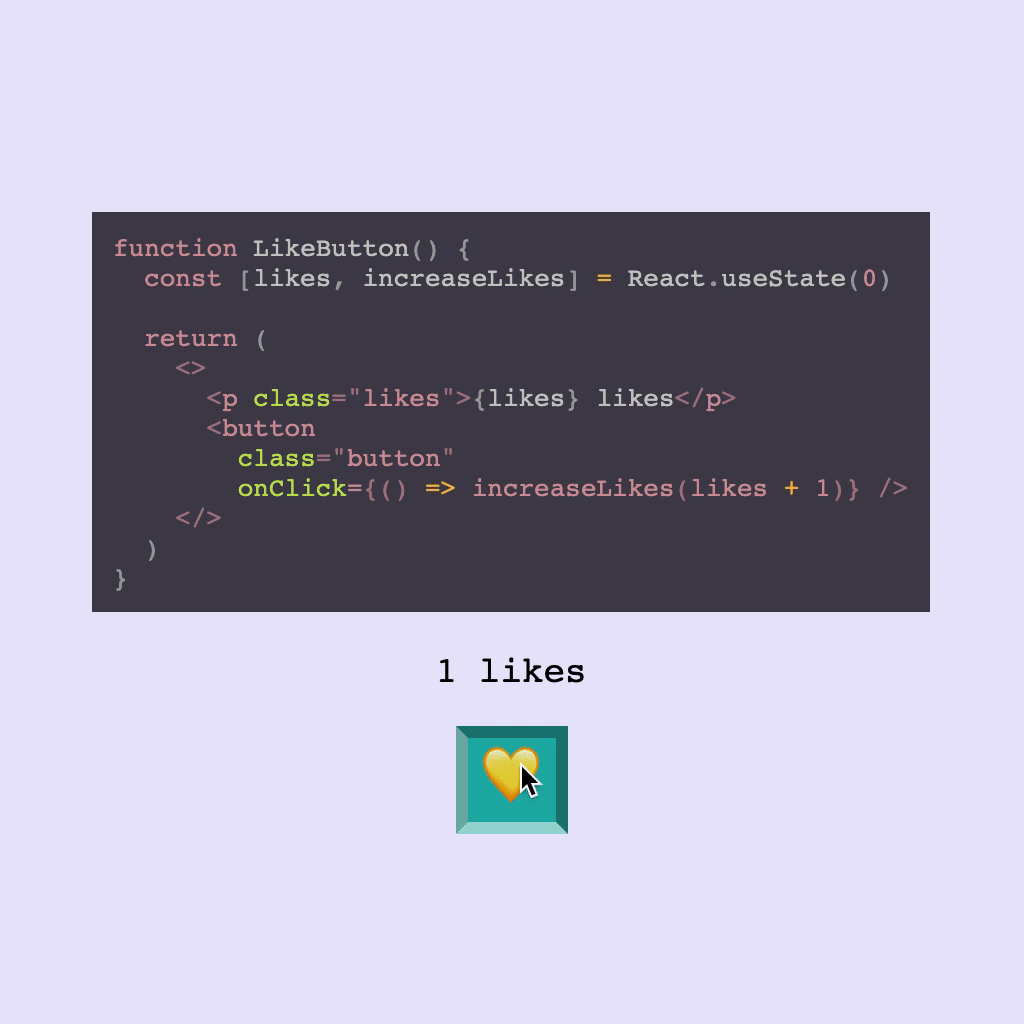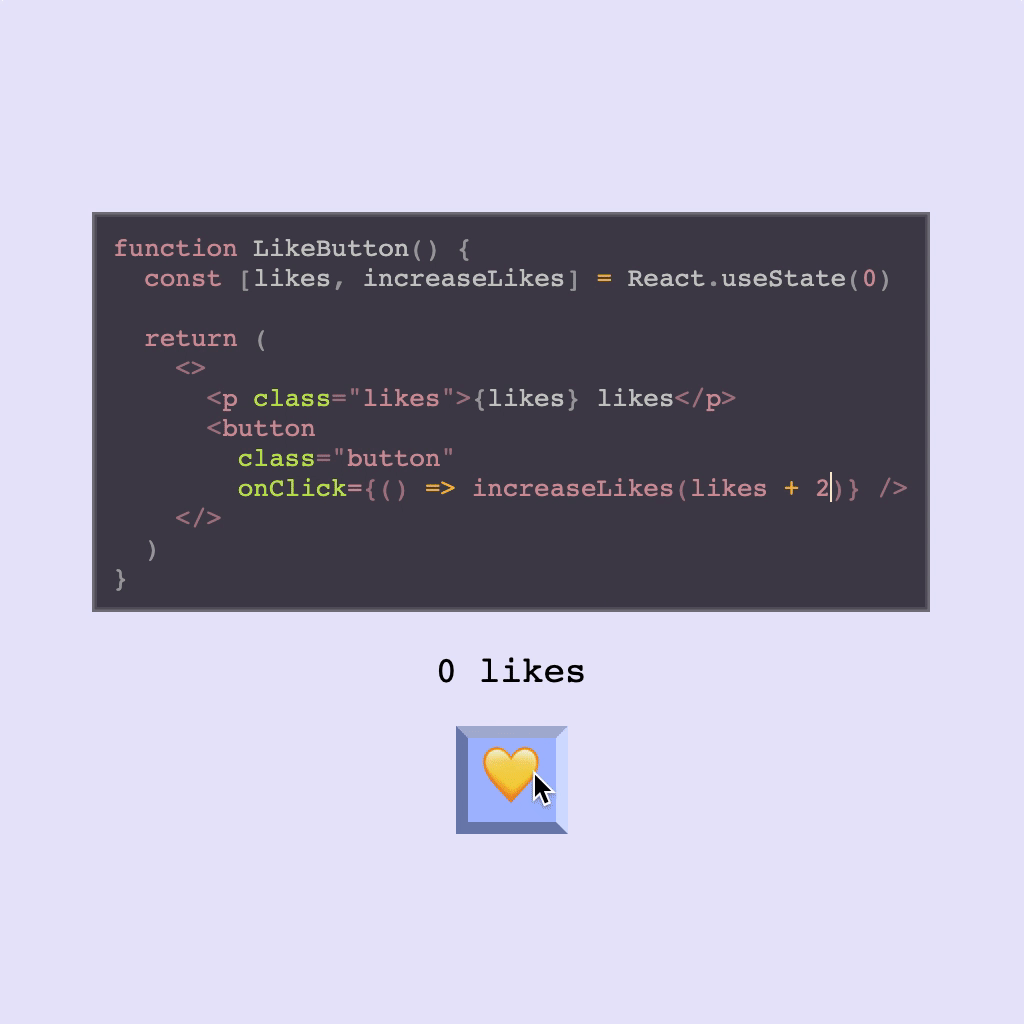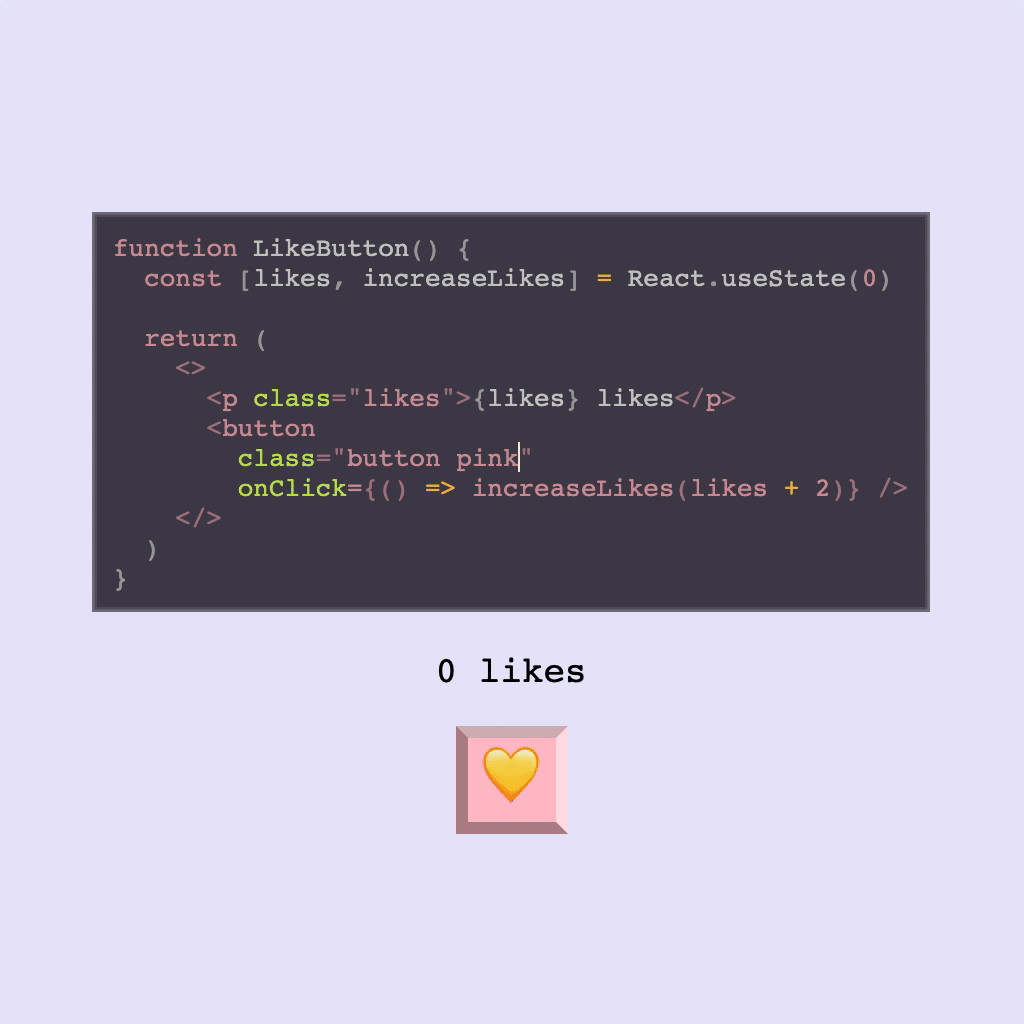
Using Hooks
React Live supports using Hooks, but you may need to be mindful of the scope. As mentioned above, only React is injected into scope by default.
This means that while you may be used to destructuring useState when importing React, to use hooks provided by React in React Live you will either need to stick to using React.useState or alternately you can set the scope up so that useState is provided separately.
- ``` js
- () => {
- const [likes, increaseLikes] = React.useState(0);
- return (
- <>
- <p>
- {`${likes} likes`}
- </p>
- <button onClick={() => increaseLikes(likes + 1)}>Like</button>
- </>
- );
- }
- ```
What bundle size can I expect?
Our reported bundle size badges don't give you the full picture of
the kind of sizes you will get in a production app. The minified
bundles we publish _exclude_ some dependencies that we depend
on.

In an actual app when you use react-live you will also be bundling
Sucrase for transpilation.
API
<LiveProvider />
This component provides the context for all the other ones. It also transpiles the user’s code!
It supports these props, while passing any others through to the children:
| |Name|PropType|Description| |
|---|
| |---|---|---| |
| |code|PropTypes.string|The |
| |scope|PropTypes.object|Accepts |
| |noInline|PropTypes.bool|Doesn’t |
| |transformCode|PropTypes.func|Accepts |
| |language|PropTypes.string|What |
| |disabled|PropTypes.bool|Disable |
| |theme|PropTypes.object|A |
All subsequent components must be rendered inside a provider, since they communicate
using one.
The noInline option kicks the Provider into a different mode, where you can write imperative-style
code and nothing gets evaluated and mounted automatically. Your example will need to call render
with valid JSX elements.
<LiveEditor />
This component renders the editor that displays the code. It is a wrapper around [react-simple-code-editor](https://github.com/satya164/react-simple-code-editor) and the code highlighted using [prism-react-renderer](https://github.com/FormidableLabs/prism-react-renderer).
| |Name|PropType|Description| |
|---|
| |---|---|---| |
| |style|PropTypes.object|Allows |
<LiveError />
This component renders any error that occur while executing the code, or transpiling it.
It passes through any props to a pre.
Note: Right now when the component unmounts, when there’s no error to be shown.
<LivePreview />
This component renders the actual component that the code generates inside an error boundary.
| |Name|PropType|Description| |
|---|
| |---|---|---| |
| |Component|PropTypes.node|Element |
withLive
The withLive method creates a higher-order component, that injects the live-editing props provided
by LiveProvider into a component.
Using this HOC allows you to add new components to react-live, or replace the default ones, with a new
desired behavior.
The component wrapped with withLive gets injected the following props:
| |Name|PropType|Description| |
|---|
| |---|---|---| |
| |code|PropTypes.string|Reflects |
| |error|PropTypes.string|An |
| |onError|PropTypes.func|A |
| |onChange|PropTypes.func|A |
| |element|React.Element|The |
Note: The code prop doesn't reflect the up-to-date code, but the code prop, that is passed to the LiveProvider.
FAQ
I want to use experimental feature x but Sucrase doesn't support it! Can I use babel instead?
react-live doesn't currently support configuring the transpiler and it ships with Sucrase. The current workaround for using some experimental features Sucrase doesn't support would be to use the transformCode prop on LiveProvider to transform your code with babel alongside Sucrase.
Comparison to component-playground
There are multiple options when it comes to live, editable React component environments. Formidable actually has two first class projects to help you out: [component-playground](https://github.com/FormidableLabs/component-playground) and [react-live](https://github.com/FormidableLabs/react-live). Let's briefly look at the libraries, use cases, and factors that might help in deciding which is right for you.
Here's a high-level decision tree:
- If you want fast and easy setup and integration, then component-playground may be the ticket!
- If you want a smaller bundle, SSR, and more flexibility, then react-live is for you!
Here are the various factors at play:
- Build: component-playground uses babel-standalone, react-live uses Sucrase.
- Bundle size: component-playground has a larger bundle, but uses a more familiar editor setup. react-live is smaller, but more customized editor around prism.
- Ease vs. flexibility: react-live is more modular/customizable, while component-playground is easier/faster to set up.
- Extra features: component-playground supports raw evaluation and pretty-printed output out-of-the-box, while react-live does not.
- Error handling: component-playground might have more predictable error handling than react-live in some cases (due to react-dom).
Maintenance Status
Active: Formidable is actively working on this project, and we expect to continue for work for the foreseeable future. Bug reports, feature requests and pull requests are welcome.
 探客时代
探客时代